Identify the audit objectives applicable to property plant and equipment Haldimand County
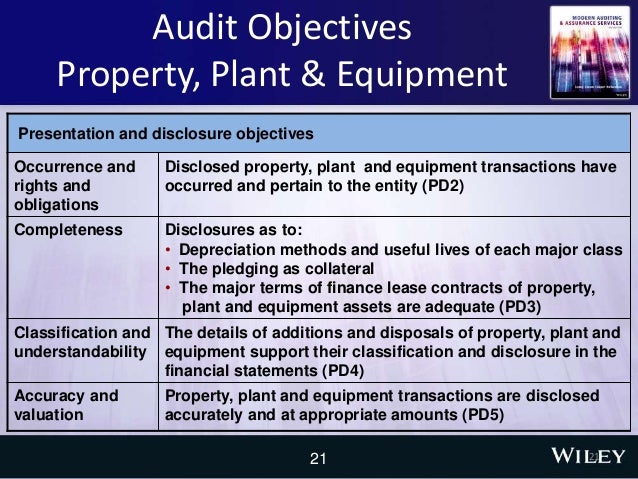
CHAPTER Property Plant and Equipment Acquisition and property, plant and equipment. 3.3 For all items acquired the values must be included in the Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register. 3.4 The Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register must at least contain the following information in line with disclosure requirements of GRAP 17.
Audit procedures ACCA Qualification Students ACCA Global
CHAPTER 10 ACCOUNTING FOR PROPERTY PLANT AND. b The primary characteristic that distinguishes property, plant, and equipment from inventory, prepaid expenses, and investments is the intention to use property, plant, and equipment as a part of the operations of the client’s business and their expected life of approximately one year. a. …, Audit Toolbox – part 1: Property, Plant and Equipment & Cash Vienna, February 12, 2014 Atanasko Atanasovski, Consultant, CFRR . Key areas when testing tangible non-current assets: Confirmation of ownership, Inspection of non-current assets, Valuation by third parties, Adequacy of depreciation rates, Potential impairment. Substantive testing - Property, plant and equipment 2 . Substantive.
Question: ACCOUNTING MAJOR - AUDIT CASE (AUDITING THE FINANCING/INVESTING PROCESS : VARIOUS ASSET ACCOUNTS Gonzales, CPA, Is The Auditor For A Manufacturing Company With A Balance Sheet That Includes The Entry “Property, Plant, And Equipment.” Gonzales Has Been Asked By The Company’s Management If Audit Adjustments Or Reclassifications Are Required For 30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it …
to ensure safe operation and maintenance of the plant. 2) Identify what people need to know to operate the plant. 3) Identify the standard of performance required for different levels of supervision. 4) Identify how and by whom their competency will be assessed. 5) Document the training required according to the HS Training Procedure. 29/08/2014 · This video explains what property, plant, and equipment means in the context of financial accounting. It also discusses how PP&E is recorded at cost …
to ensure safe operation and maintenance of the plant. 2) Identify what people need to know to operate the plant. 3) Identify the standard of performance required for different levels of supervision. 4) Identify how and by whom their competency will be assessed. 5) Document the training required according to the HS Training Procedure. to ensure safe operation and maintenance of the plant. 2) Identify what people need to know to operate the plant. 3) Identify the standard of performance required for different levels of supervision. 4) Identify how and by whom their competency will be assessed. 5) Document the training required according to the HS Training Procedure.
This Subtopic provides accounting guidance for the sale of real estate other than retail land. The real estate sales guidance was placed under the Property, Plant, and Equipment Topic because it is applicable to all entities involved with real estate sales transactions. Chapter 10 Property, Plant, and Equipment Chapter 10 - 4 (2) A property record unit, sometimes called a PP&E record unit, is a plant or equipment item, for example, a building, selected to be continuously identified in the property records. The selection of property record …
Chapter 10 Property, Plant, and Equipment Chapter 10 - 4 (2) A property record unit, sometimes called a PP&E record unit, is a plant or equipment item, for example, a building, selected to be continuously identified in the property records. The selection of property record … When audits are scheduled, PMO will give as much advance notification to the department as possible. The DPA should be actively involved and may be requested to participate as an escort. They must be able to locate and identify property as requested by auditors and be able to provide supporting documentation upon request. If the DPA cannot
Internal Audit Checklist: Property, Plant, and Equipment Investments February 27, 2019 February 27, 2019 Vonya Global In general, the objective of an internal audit is to assess the risk of material misstatement in financial reporting. 31/12/2004 · Topic 11 notes and question on ppe 1. AUD390 AUDIT OF PROPERTY PLANT & EQUIPMENT MAIN OBJECTIVES OF CONTROL OVER PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT To ensure all acquisitions are properly authorized. To safeguard all the assets. To ensure all assets are properly recorded. To ensure assets are written off over their useful life. Appropriate depreciation i.e. adequate …
30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it … EC staff consolidated version as of 16 September 2009 Last EU endorsed/amended on 12.06.2009. Objective. 1The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for property, plant and equipment so that users of the financial statements can discern information about an entity’s investment in its property, plant and equipment and the changes in such investment.
Property, plant and equipment (also called tangible fixed assets) is a class of assets which have physical existence, which are held for a company’s internal use and which are expected to generate economic benefits for the company over more than one year. Chapter 10, Accounting for Property, Plant and Equipment . 10-5 . is not limited to, landscaping, sidewalks, parking lots, furniture, fixtures and network equipment. Assets acquired through bulk or aggregate purchases may be grouped into one or more property record units in accordance with the guidance in section 2k of this . policy.
Chapter 13 Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Answer Key True / False Questions 1. The auditors' approach to the audit of property, plant and equipment largely results from the fact that relatively few transactions occur. TRUE Difficulty: Easy 2. A major control procedure related to plant and equipment is a budget for Accuracy of Property, Plant, and Equipment Financial Information 1. As part of our audit of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Fiscal Year (FY) 1997 Consolidated Financial Statements (CFS), we evaluated management’s internal control structure over property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). In addition, we made an
IAS 16 outlines the accounting treatment for most types of property, plant and equipment. Property, plant and equipment is initially measured at its cost, subsequently measured either using a cost or revaluation model, and depreciated so that its depreciable amount is allocated on a systematic basis over its useful life. IAS 16 was reissued in December 2003 and applies to annual periods This Subtopic provides accounting guidance for the sale of real estate other than retail land. The real estate sales guidance was placed under the Property, Plant, and Equipment Topic because it is applicable to all entities involved with real estate sales transactions.
to the accounting for property, plant and equipment contained in HKAS 16. The main features IN4 The main features of HKAS 16 are described below. Scope IN5 This Standard clarifies that an entity is required to apply the principles of this Standard to items of property, plant and equipment used to develop or maintain (a) biological assets and (b) Audit Toolbox – part 1: Property, Plant and Equipment & Cash Vienna, February 12, 2014 Atanasko Atanasovski, Consultant, CFRR . Key areas when testing tangible non-current assets: Confirmation of ownership, Inspection of non-current assets, Valuation by third parties, Adequacy of depreciation rates, Potential impairment. Substantive testing - Property, plant and equipment 2 . Substantive
Audit Toolbox part 1 Property Plant and Equipment & Cash
Audit procedures ACCA Qualification Students ACCA Global. The subject matter for discussion on audit readiness this week is Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE). This item falls within the scope of IAS 16. This standard is applicable in accounting for property, plant and equipment, which it defines as tangible items that:, b The primary characteristic that distinguishes property, plant, and equipment from inventory, prepaid expenses, and investments is the intention to use property, plant, and equipment as a part of the operations of the client’s business and their expected life of approximately one year. a. ….
Property Plant and Equipment (Chapter 13 Auditing. The subject matter for discussion on audit readiness this week is Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE). This item falls within the scope of IAS 16. This standard is applicable in accounting for property, plant and equipment, which it defines as tangible items that:, This CPE course can be purchased individually or as part of the Audit Staff Essentials – New Staff: Practical Application staff training bundle.. The basic accounting for property, plant, and equipment is fairly straightforward, but you have to be alert for unusual or complex transactions, such as exchanges, capitalized interest, or sale-leasebacks..
3.9 Property Audits DoResearch

Recorded additions represent property plant and equipment. We argue that fair value measures for property, plant, and equipment are superior to historical cost based on the characteristics of predictive value, feedback value, timeliness, neutrality IAS 16 outlines the accounting treatment for most types of property, plant and equipment. Property, plant and equipment is initially measured at its cost, subsequently measured either using a cost or revaluation model, and depreciated so that its depreciable amount is allocated on a systematic basis over its useful life. IAS 16 was reissued in December 2003 and applies to annual periods.

We argue that fair value measures for property, plant, and equipment are superior to historical cost based on the characteristics of predictive value, feedback value, timeliness, neutrality identify the audit objectives applicable to property plant equipment ppe 40 from accounting ayb301 at queensland
This Subtopic provides accounting guidance for the sale of real estate other than retail land. The real estate sales guidance was placed under the Property, Plant, and Equipment Topic because it is applicable to all entities involved with real estate sales transactions. Property, plant and equipment (also called tangible fixed assets) is a class of assets which have physical existence, which are held for a company’s internal use and which are expected to generate economic benefits for the company over more than one year.
This Subtopic provides accounting guidance for the sale of real estate other than retail land. The real estate sales guidance was placed under the Property, Plant, and Equipment Topic because it is applicable to all entities involved with real estate sales transactions. property, plant and equipment. 3.3 For all items acquired the values must be included in the Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register. 3.4 The Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register must at least contain the following information in line with disclosure requirements of GRAP 17.
This Subtopic provides accounting guidance for the sale of real estate other than retail land. The real estate sales guidance was placed under the Property, Plant, and Equipment Topic because it is applicable to all entities involved with real estate sales transactions. Today, I tell you how to audit plant, property, and equipment (or capital assets if you work with governments). Plant, property, and equipment is often the largest item on a balance sheet. But the risk is often low to moderate. After all, it’s difficult to steal land or a building. And the accounting is usually not difficult. So the dollar amount can be high but the risk low.
Chapter 10, Accounting for Property, Plant and Equipment . 10-5 . is not limited to, landscaping, sidewalks, parking lots, furniture, fixtures and network equipment. Assets acquired through bulk or aggregate purchases may be grouped into one or more property record units in accordance with the guidance in section 2k of this . policy. Internal Audit Checklist: Property, Plant, and Equipment Investments February 27, 2019 February 27, 2019 Vonya Global In general, the objective of an internal audit is to assess the risk of material misstatement in financial reporting.
property, plant and equipment. 3.3 For all items acquired the values must be included in the Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register. 3.4 The Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register must at least contain the following information in line with disclosure requirements of GRAP 17. Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Review Questions 13–1 Factors that facilitate the auditors' verification of plant and equipment but are not applicable to audit work on current assets include the following: (1) High dollar amount of individual items. A relatively few transactions may support a large balance sheet amount.
IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment × Show Sections holding themselves out as representatives and/or independent agents of the IASB and purporting to undertake financial audits of investment companies on our behalf. These individuals do not represent either the IFRS Foundation and/or the IASB, neither of whom conduct such range of activities. In the event that you have received such Chapter 10 Property, Plant, and Equipment Chapter 10 - 4 (2) A property record unit, sometimes called a PP&E record unit, is a plant or equipment item, for example, a building, selected to be continuously identified in the property records. The selection of property record …
30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it … property, plant and equipment. 3.3 For all items acquired the values must be included in the Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register. 3.4 The Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register must at least contain the following information in line with disclosure requirements of GRAP 17.
This CPE course can be purchased individually or as part of the Audit Staff Essentials – New Staff: Practical Application staff training bundle.. The basic accounting for property, plant, and equipment is fairly straightforward, but you have to be alert for unusual or complex transactions, such as exchanges, capitalized interest, or sale-leasebacks. We argue that fair value measures for property, plant, and equipment are superior to historical cost based on the characteristics of predictive value, feedback value, timeliness, neutrality
30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it … Analytical procedures were also used during the substantive testing phase to audit the increases in property, plant, and equipment. After the testing, BK&D determined that they had met the audit standard requirements as they had performed two sets of analytical procedures. 1.) What step did BK&D CPAs fail to perform? 2.) Why do audit standards

Internal Audit Checklist: Property, Plant, and Equipment Investments February 27, 2019 February 27, 2019 Vonya Global In general, the objective of an internal audit is to assess the risk of material misstatement in financial reporting. requirements, property transfers, research of unallocated and missing assets, and asset disposals and recordkeeping. OBJECTIVE, SCOPE, AND METHODOLOGY The main objective of this audit is to identify best practices for potential improvements to incorporate into District practices. The audit provides an independent review of the District’s
CHAPTER 9 AUDITING THE REVENUE CYCLE audit-uii.yolasite.com
Topic 11 notes and question on ppe SlideShare. Property, plant and equipment (also called tangible fixed assets) is a class of assets which have physical existence, which are held for a company’s internal use and which are expected to generate economic benefits for the company over more than one year., 07/03/2010 · AUDIT PROGRAM PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT GUIDANCE The auditor should consider the nature of the account balance and the risks associated with transactions flowing through it. The steps in this area may also be applied to capitalized leases. When preparing this program the auditor should consider and design audit.
Audit Toolbox part 1 Property Plant and Equipment & Cash
GUIDANCE NOTE ON AUDIT OF PROPERTY PLANT & EQUIPMENT. to ensure safe operation and maintenance of the plant. 2) Identify what people need to know to operate the plant. 3) Identify the standard of performance required for different levels of supervision. 4) Identify how and by whom their competency will be assessed. 5) Document the training required according to the HS Training Procedure., This sample audit work program primarily focuses on the existence, additions, disposals, and depreciation of fixed assets and leases. The objectives of this audit program are to: determine that the property exists and is owned by the business unit; determine that additions to property are authentic, recorded at cost and properly distinguished from maintenance and repairs expenses; determine.
Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Review Questions 13–1 Factors that facilitate the auditors' verification of plant and equipment but are not applicable to audit work on current assets include the following: (1) High dollar amount of individual items. A relatively few transactions may support a large balance sheet amount. 07/03/2010 · AUDIT PROGRAM PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT GUIDANCE The auditor should consider the nature of the account balance and the risks associated with transactions flowing through it. The steps in this area may also be applied to capitalized leases. When preparing this program the auditor should consider and design audit
requirements, property transfers, research of unallocated and missing assets, and asset disposals and recordkeeping. OBJECTIVE, SCOPE, AND METHODOLOGY The main objective of this audit is to identify best practices for potential improvements to incorporate into District practices. The audit provides an independent review of the District’s The subject matter for discussion on audit readiness this week is Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE). This item falls within the scope of IAS 16. This standard is applicable in accounting for property, plant and equipment, which it defines as tangible items that:
Today, I tell you how to audit plant, property, and equipment (or capital assets if you work with governments). Plant, property, and equipment is often the largest item on a balance sheet. But the risk is often low to moderate. After all, it’s difficult to steal land or a building. And the accounting is usually not difficult. So the dollar amount can be high but the risk low. We argue that fair value measures for property, plant, and equipment are superior to historical cost based on the characteristics of predictive value, feedback value, timeliness, neutrality
requirements, property transfers, research of unallocated and missing assets, and asset disposals and recordkeeping. OBJECTIVE, SCOPE, AND METHODOLOGY The main objective of this audit is to identify best practices for potential improvements to incorporate into District practices. The audit provides an independent review of the District’s This CPE course can be purchased individually or as part of the Audit Staff Essentials – New Staff: Practical Application staff training bundle.. The basic accounting for property, plant, and equipment is fairly straightforward, but you have to be alert for unusual or complex transactions, such as exchanges, capitalized interest, or sale-leasebacks.
Audit Toolbox – part 1: Property, Plant and Equipment & Cash Vienna, February 12, 2014 Atanasko Atanasovski, Consultant, CFRR . Key areas when testing tangible non-current assets: Confirmation of ownership, Inspection of non-current assets, Valuation by third parties, Adequacy of depreciation rates, Potential impairment. Substantive testing - Property, plant and equipment 2 . Substantive b The primary characteristic that distinguishes property, plant, and equipment from inventory, prepaid expenses, and investments is the intention to use property, plant, and equipment as a part of the operations of the client’s business and their expected life of approximately one year. a. …
This Revised ‘Accounting Standards (AS 10 – Property, Plant and Equipment’ is applicable for the accounting periods commencing on or after April 1, 2017 after considering Companies (Accounting Standards) Amendment Rules, 2016 (G.S.R. 364(E) dated 30.03.2016) read with ICAI Press Release dated 28.09.2016 titled “ Amendment to AS 2, 4, 6, 10, 13, 14, 21 and 29 issued by the Institute of property, plant and equipment. 3.3 For all items acquired the values must be included in the Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register. 3.4 The Property, Plant and Equipment Asset Register must at least contain the following information in line with disclosure requirements of GRAP 17.
29/08/2014 · This video explains what property, plant, and equipment means in the context of financial accounting. It also discusses how PP&E is recorded at cost … 30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it …
Question: ACCOUNTING MAJOR - AUDIT CASE (AUDITING THE FINANCING/INVESTING PROCESS : VARIOUS ASSET ACCOUNTS Gonzales, CPA, Is The Auditor For A Manufacturing Company With A Balance Sheet That Includes The Entry “Property, Plant, And Equipment.” Gonzales Has Been Asked By The Company’s Management If Audit Adjustments Or Reclassifications Are Required For Chapter 10, Accounting for Property, Plant and Equipment . 10-5 . is not limited to, landscaping, sidewalks, parking lots, furniture, fixtures and network equipment. Assets acquired through bulk or aggregate purchases may be grouped into one or more property record units in accordance with the guidance in section 2k of this . policy.
The auditors' verification of plant and equipment is facilitated by several factors not applicable to audit work on current assets. What are these factors? What are these factors? The audit work required to verify PP&E is usually a much smaller proportion of the total audit … disposed item of property, plant and equipment. IN14. The Standard requires an entity to derecognize the carrying amount of a part of an item of property, plant and equipment if that part has been replaced and the entity has included the cost of the replacement in the carrying amount of the item (see paragraph 85). Previously, IPSAS 17 did
A practical guide to accounting for property under the cost model PricewaterhouseCoopers 2 Introduction IAS 16, ‘Property, plant and equipment’ includes guidance on how to account for property carried at cost. IAS 16 applies to property (that is, buildings) held … IAS 16 outlines the accounting treatment for most types of property, plant and equipment. Property, plant and equipment is initially measured at its cost, subsequently measured either using a cost or revaluation model, and depreciated so that its depreciable amount is allocated on a systematic basis over its useful life. IAS 16 was reissued in December 2003 and applies to annual periods
Auditing Property Plant and Equipment - Blogger. Accuracy of Property, Plant, and Equipment Financial Information 1. As part of our audit of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Fiscal Year (FY) 1997 Consolidated Financial Statements (CFS), we evaluated management’s internal control structure over property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). In addition, we made an, View Notes - Chapter_16_updated.pptx from ACC 301 at HELP University. Chapter 16 Auditing Inventories and property, plant and equipment Objectives Identify the audit objectives applicable to.
Property Plant and Equipment – PP&E Definition

IPSAS 17—PROPERTY PLANT AND EQUIPMENT IFAC. Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Review Questions 13–1 Factors that facilitate the auditors' verification of plant and equipment but are not applicable to audit work on current assets include the following: (1) High dollar amount of individual items. A relatively few transactions may support a large balance sheet amount., Chapter 13 Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Answer Key True / False Questions 1. The auditors' approach to the audit of property, plant and equipment largely results from the fact that relatively few transactions occur. TRUE Difficulty: Easy 2. A major control procedure related to plant and equipment is a budget for.
CHAPTER 9 AUDITING THE REVENUE CYCLE audit-uii.yolasite.com

Auditing Property Plants and Equipment Auditing and. b The primary characteristic that distinguishes property, plant, and equipment from inventory, prepaid expenses, and investments is the intention to use property, plant, and equipment as a part of the operations of the client’s business and their expected life of approximately one year. a. … When audits are scheduled, PMO will give as much advance notification to the department as possible. The DPA should be actively involved and may be requested to participate as an escort. They must be able to locate and identify property as requested by auditors and be able to provide supporting documentation upon request. If the DPA cannot.

Analytical procedures were also used during the substantive testing phase to audit the increases in property, plant, and equipment. After the testing, BK&D determined that they had met the audit standard requirements as they had performed two sets of analytical procedures. 1.) What step did BK&D CPAs fail to perform? 2.) Why do audit standards Auditing - Property, Plant and Equipment How do auditors audit property, plant and equipment (PPE) or the one used to be called fixed assets? Since audit is an art, each accounting firm has their own procedures to audit property, plant and equipment.
to the accounting for property, plant and equipment contained in HKAS 16. The main features IN4 The main features of HKAS 16 are described below. Scope IN5 This Standard clarifies that an entity is required to apply the principles of this Standard to items of property, plant and equipment used to develop or maintain (a) biological assets and (b) EC staff consolidated version as of 16 September 2009 Last EU endorsed/amended on 12.06.2009. Objective. 1The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for property, plant and equipment so that users of the financial statements can discern information about an entity’s investment in its property, plant and equipment and the changes in such investment.
Analytical procedures were also used during the substantive testing phase to audit the increases in property, plant, and equipment. After the testing, BK&D determined that they had met the audit standard requirements as they had performed two sets of analytical procedures. 1.) What step did BK&D CPAs fail to perform? 2.) Why do audit standards The subject matter for discussion on audit readiness this week is Property, Plant and Equipment (PPE). This item falls within the scope of IAS 16. This standard is applicable in accounting for property, plant and equipment, which it defines as tangible items that:
Chapter 10, Accounting for Property, Plant and Equipment . 10-5 . is not limited to, landscaping, sidewalks, parking lots, furniture, fixtures and network equipment. Assets acquired through bulk or aggregate purchases may be grouped into one or more property record units in accordance with the guidance in section 2k of this . policy. Audit readiness (3) Investment Property. Adequate documentation must be in place to support the assumption that Investment properties reflect the existing business circumstances and economic conditions in accordance with the accounting policies being used. The subject matter for discussion on audit readiness this week is Investment Property. This item falls within the scope of IAS 40
Property, plant and equipment (also called tangible fixed assets) is a class of assets which have physical existence, which are held for a company’s internal use and which are expected to generate economic benefits for the company over more than one year. This sample audit work program primarily focuses on the existence, additions, disposals, and depreciation of fixed assets and leases. The objectives of this audit program are to: determine that the property exists and is owned by the business unit; determine that additions to property are authentic, recorded at cost and properly distinguished from maintenance and repairs expenses; determine
Accuracy of Property, Plant, and Equipment Financial Information 1. As part of our audit of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Fiscal Year (FY) 1997 Consolidated Financial Statements (CFS), we evaluated management’s internal control structure over property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). In addition, we made an 30/07/2017 · Property, plant, and equipment generally termed as PPE has been an influential contributor of the asset side of balance sheet( Statement of Financial Position).Even it …
LEARNING OBJECTIVES . 8. Determine and apply sufficient appropriate substantive audit procedures for testing revenue cycle accounts, disclosures, and assertions . 9. Apply the frameworks for professional decision making and ethical decision making to issues involving the audit of revenue cycle accounts, disclosures, and assertions 07/03/2010 · AUDIT PROGRAM PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT GUIDANCE The auditor should consider the nature of the account balance and the risks associated with transactions flowing through it. The steps in this area may also be applied to capitalized leases. When preparing this program the auditor should consider and design audit
18/11/2017 · These include patents, copyrights, catalog costs, and all property, plant, and equipment accounts. In the audit of equipment and related accounts, it is helpful to separate the tests into the Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are long-term assets vital to business operations and not easily converted into cash. Purchases of PP&E are a signal that management has faith in the long
The auditors' verification of plant and equipment is facilitated by several factors not applicable to audit work on current assets. What are these factors? What are these factors? The audit work required to verify PP&E is usually a much smaller proportion of the total audit … Property, Plant, and Equipment: Depreciation and Depletion Review Questions 13–1 Factors that facilitate the auditors' verification of plant and equipment but are not applicable to audit work on current assets include the following: (1) High dollar amount of individual items. A relatively few transactions may support a large balance sheet amount.
18/11/2017 · These include patents, copyrights, catalog costs, and all property, plant, and equipment accounts. In the audit of equipment and related accounts, it is helpful to separate the tests into the Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are long-term assets vital to business operations and not easily converted into cash. Purchases of PP&E are a signal that management has faith in the long
Chapter 10 Property, Plant, and Equipment Chapter 10 - 4 (2) A property record unit, sometimes called a PP&E record unit, is a plant or equipment item, for example, a building, selected to be continuously identified in the property records. The selection of property record … When audits are scheduled, PMO will give as much advance notification to the department as possible. The DPA should be actively involved and may be requested to participate as an escort. They must be able to locate and identify property as requested by auditors and be able to provide supporting documentation upon request. If the DPA cannot


